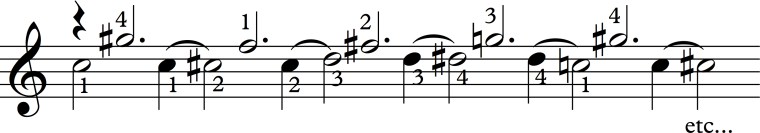Brought to public light by the great maestro Alirio Diaz decades ago, Venezuelan composer Antonio Lauro’s beloved Natalia (aka Valse Criollo and Valse Venezolano Nº3) has become one of the most widely played pieces on our instrument.
There are so many thoughts to share on this piece with students that I thought I’d do a short (which is now looking long) post about a passage in the first part of the piece that most students wrestle with as they begin to enjoy their discovery of Venezuelan guitar music.
To begin, the initial published edition by Broekmans & Van Poppel B.V. and the more recent edition published by Ediciones Caroní differ in several ways. It is important to note that both were revised by Alirio Diaz who over the decades has probably played this piece thousands of times. And, over the course of Alirio’s history with the piece, he has undoubtably made changes simply to keep the piece evolving in a creative way. Is the latest version better? Not necessarily. However, students should become intimately familiar with both and with alternate fingerings that may help them achieve their own musical goals.
It is important to mention that scores are often a very close approximation of the intent of the composer. In guitar scores, because of the fact that composers are cramming everything onto one staff, short hand helps musicians see through the clutter of notating all voices accurately. So with that caveat…
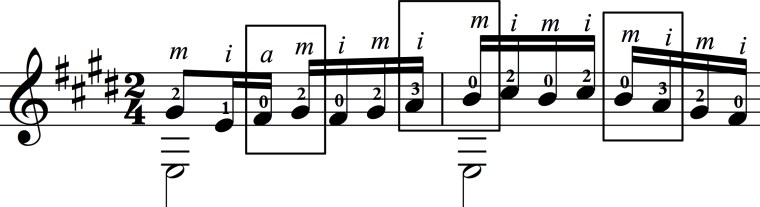
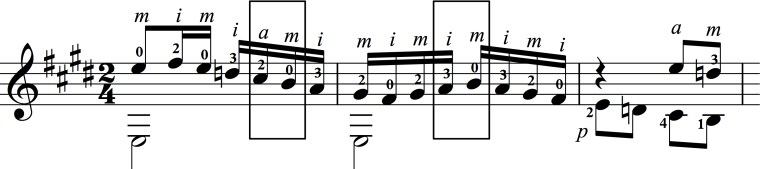
Here is the passage we’re studying from the first two editions for comparison:
Broekmans & Van Poppel B.V.

Ediciones Caroní

The differences are interesting to say the least. The fingering has evolved which, of course, is a natural thing to occur after years of playing the same piece. But, of note, notice the rhythmic changes with the beaming. Antonio Lauro’s music is always full of the dueling time signatures 3/4 and 6/8 which makes his and other Venezuelan music so alluring on a rhythmic front. There is a very different feel when playing the first measure of this passage.
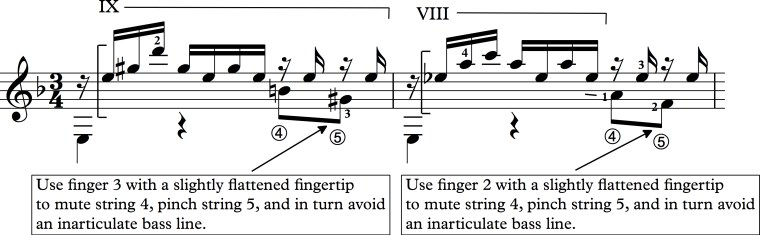
When I initially learned Natalia decades ago, like most students, I used what was available. For the most part, I followed Alirio’s fingerings closely. However, as my hands have come into their own over the years, my version has evolved quite a bit to suit my strengths, technique, fingers, and musical ideas. Here are two ways I tend to play it these days:


The differences have evolved to help me feel more secure as I play the piece. Notice the guide fingers throughout.
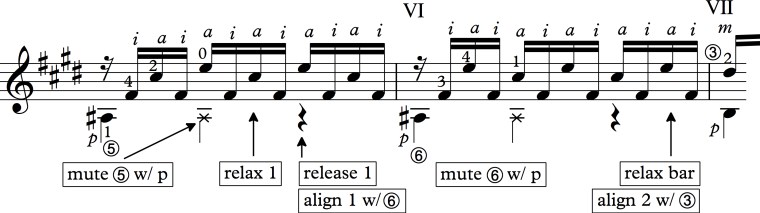
As students uncover their own interpretations, I often make sure that they are aurally aware of as much as possible so that if they wanted to draw attention to a particular voice for any reason, they could do so. As much as I like the groovy and energetic way Alirio plays the piece, I often like hearing a more legato version so I try to keep my ear on the following voice:

Despite the fact that they are written as eighth notes, I often try to connect the line. Did Lauro intend to break the line? Not sure. Can I play it both ways? Yes. Which do I like best? Depends on how I feel.
Another voice I like to draw attention to is this one:

This was intended to be a MINI masterclass so I’m going to wrap this up. The bottom line is that pieces evolve in the musician’s hand. Spend time exploring the history of the pieces you are playing, and specifically with Natalia, the possibilities, fingerings, and seeing which rhythmic version feels right, and you will be on your way to crafting a meaningful interpretation that you can stand behind when sharing it with others.

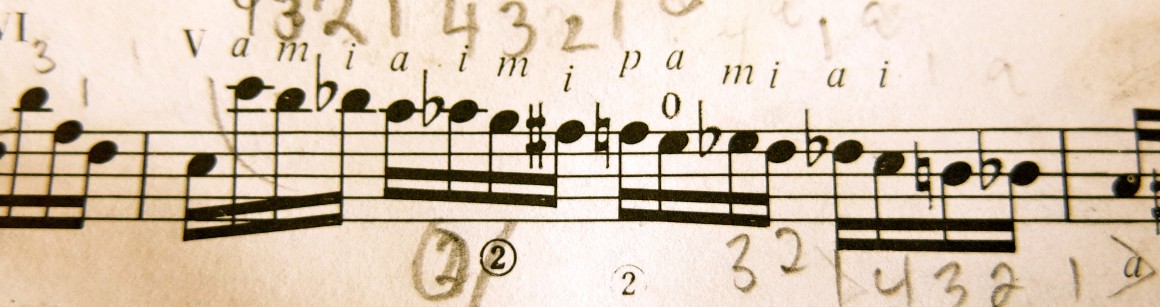












 Rule 2
Rule 2